
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Laser Materials and Devices, Jiangsu Normal University, Xuzhou 221116, China
2 College of Electronic and Information Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
3 Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Laser Technology and Emerging Industry, Jiangsu Normal University, Xuzhou 221116, China
In this paper, we report on a wide wavelength tuning optical vortex carrying orbital angular momentum (OAM) of ±ħ, from a thulium-doped yttrium aluminum perovskite (YAP) laser employing a birefringent filter. The OAM is experimentally found to be well maintained during the whole wavelength tuning process. The Laguerre–Gaussian () mode with a tuning range of 58 nm from 1934.8 to 1993.0 nm and mode with a range of 76 nm from 1920.4 to 1996.6 nm, are, respectively, obtained. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first experimental implementation of wavelength tuning for a scalar vortex laser in the 2 µm spectral range, as well as the broadest tuning range ever reported from the vortex laser cavity. Such a vortex laser with robust structure and straightforward wavelength tuning capability will be an ideal light source for potential applications in the field of optical communication with one additional degree of freedom.
wavelength tunable laser 2 µm laser orbital angular momentum Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(2): 021405

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronic and Information Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Light Manipulations and Applications, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
3 Key Laboratory of Transparent and Opto-functional Inorganic Materials, Artificial Crystal Research Center, Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200050, China
4 School of Physics and Astronomy, Yunnan University, Kunming 650091, China
The anisotropy of thermal property in an crystal is investigated from the temperature of 293 to 573 K. Based on the systematical study of thermal expansion, thermal diffusivity, and specific heat, the thermal conductivity in crystals orientated at (100), (010), (001), and (406) is calculated to be 3.46, 2.60, 3.35, and , respectively. The laser output anisotropy of a continuous-wave (CW) and tunable laser is characterized, accordingly. A maximum output power of 6.09 W is achieved in the crystal with (010) direction, corresponding to a slope efficiency of 48.56%. The tuning wavelength range in the crystal orientated at (100), (010), and (001) is 68, 67, and 65 nm, separately. The effects of thermal properties on CW laser performance are discussed.
anisotropy thermal property tunable laser Yb,Nd:Sc2SiO5 crystal Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(4): 041405
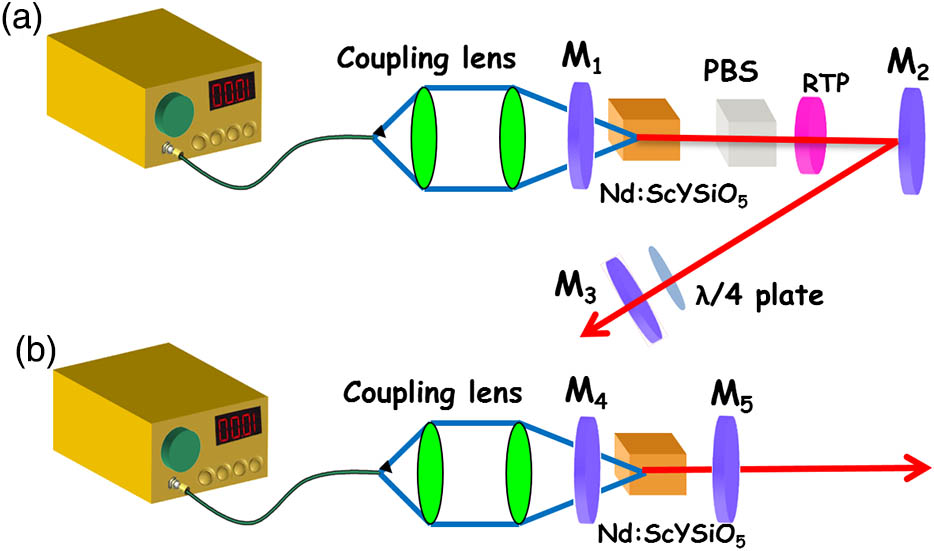
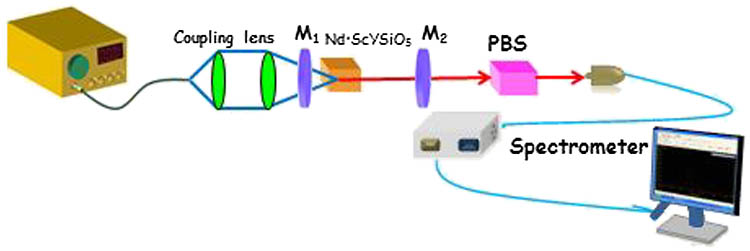
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electrical Engineering and Automation, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
2 College of Electronic and Information Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
With a Nd:ScYSiO5 crystal, a high peak power electro-optically Q-switched 1.0 μm laser and tri-wavelength laser operations at the 1.3 μm band are both investigated. With a rubidium titanyle phosphate (RTP) electro-optical switcher and a polarization beam splitter, a high signal-to-noise ratio 1.0 μm laser is obtained, generating a shortest pulse width of 30 ns, a highest pulse energy of 0.765 mJ, and a maximum peak power of 25.5 kW, respectively. The laser mode at the highest laser energy level is the TEM00 mode with the M2 value in the X and Y directions to be Mx2 = 1.52 and My2 = 1.54. A tri-wavelength Nd:ScYSiO5 crystal laser at 1.3 μm is also investigated. A maximum tri-wavelength output power is 1.03 W under the absorbed pump power of 7 W, corresponding to a slope efficiency of 14.8%. The properties of the output wavelength are fully studied under different absorbed pump power.
140.3380 Laser materials 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(11): 111403
山东科技大学电子信息工程学院, 青岛市太赫兹技术重点实验室, 青岛 266590
提出了一种基于狄拉克半金属超材料的双开口环结构的宽带偏振器,研究了狄拉克半金属费米能级以及中间介质厚度对偏振转换性能的影响。结果表明:当中间介质厚度为22 μm,费米能级为70 meV时,在1.44 THz和1.95 THz两个谐振频率处,偏振转换效率为100%;当中间介质厚度为22 μm时,随着狄拉克半金属费米能级从64 meV增加到70 meV,高低两个谐振峰均产生蓝移;当狄拉克半金属费米能级为70 meV时,随着基底介质厚度从19 μm增加到22 μm,低频处的谐振峰未移动,高频率点处的谐振峰红移。
太赫兹技术 超材料 偏振 狄拉克半金属
1 山东科技大学 a.电子通信与物理学院
2 b.青岛市太赫兹技术重点实验室,山东青岛 266510
基于石墨烯电导率的可调性,设计了 T型石墨烯纳米超材料结构,实现对电磁诱导透明(EIT)效应的动态调谐。研究发现,当 2个石墨烯条互相靠近时,由于二者间存在较强耦合,发生相消干涉,因此出现透明窗口。同时讨论了石墨烯条长度、缝宽、入射偏振角等几何参数对 EIT效应的影响。研究结果表明,耦合强度随着缝宽的增加而减弱;随着入射偏振角的增加也呈现减弱趋势;随着石墨烯条长度的增加,透明窗口发生红移现象,且第一个下降峰强度明显增加。此外,当费米能级由 0.3 eV增加到 0.9 eV时,共振频率由 24 THz蓝移至 35 THz,且强度增强,证实了改变石墨烯的费米能级,能够调节透明窗口的位置。并且透明窗口附近有明显的群速度延迟(0.05 ps左右),即可以实现对光速的减慢。
石墨烯 超材料 电磁诱导透明 graphene metamaterial Electromagnetically Induced Transparency 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报
2017, 15(2): 192
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronic, Communication and Physics, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
2 Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai 200050, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Crystal Materials, Shandong University, Ji’nan 250100, China
In this Letter, we demonstrate the anisotropy of laser emission in disordered Nd:ScYSiO5 (Nd:SYSO) crystals cut along the optical indicatrix axes. High-powered lasers with different oscillation wavelengths and polarizations are realized by using different oriented crystals as gain media. For Y-cut crystals, the dual-wavelength laser vibration direction is found to be along the X axis and a maximum output power of 9.43 W is obtained, giving an optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 48.8% and a slope efficiency of 51.3%. For X- and Z-cut crystals, 1075 and 1078 nm lasers operating orthogonally polarize oscillate with total output powers of 7.07 and 8.43 W, respectively. The experimental results reveal that the intrinsic anisotropy for the monoclinic disordered laser crystals could make laser design flexible and controllable.
140.3380 Laser materials 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(2): 021406
山东科技大学电子通信与物理学院青岛市太赫兹技术重点实验室, 山东 青岛 266510
目前人们已经实现了很高的调制深度,但是缺少对如何实现调制深度可调的研究,不利于实现波整形。利用石墨烯的电调谐性以及石墨烯超材料的表面等离激元(SPP)共振特性,设计了一种能够在某一频率实现调制深度可调的调制器,且调制深度为极大值,便于取样及检测,并运用谐振子模型对透射规律进行了理论分析。基于三维电磁场仿真软件时域求解器仿真,得到了对应频率为11.85 THz的一系列的调制深度,其中最大调制深度可达到96%以上。这一系列的调制深度可以通过电压调节石墨烯的费米能级来进行调制转换,将极大地促进调制器在波整形中的应用,如生成正弦波、三角波及方波等。此外,这种结构可以实现类电磁感应透明(EIT)现象,不仅能够实现透射峰的频移和展宽,而且可以使展宽前后的中心频率保持一致。
材料 石墨烯 超材料 调制深度 可调性 光学学报
2016, 36(10): 1016002
1 山东科技大学理学院山东省太赫兹技术重点实验室青岛市太赫兹技术重点实验室, 山东 青岛 266590
2 天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院激光与光电子研究所光电信息技术教育部重点实验室, 天津 300072
理论分析了双光子和三光子吸收对非线性材料差频产生太赫兹(THz)波的影响,在不同抽运功率下,计算了相位失配情况下晶体的最佳作用长度和THz 的最大量子转化效率,并将其与相位匹配情况进行对比。研究结果表明,抽运功率不太高时,多光子吸收对差频产生THz 波影响不大;随着抽运功率的提高,多光子吸收的影响变得显著;抽运功率较高时,相位匹配与相位失配情况下,双光子和三光子吸收效应都增加了晶体的最佳作用长度,降低了THz 的最大转化效率。研究了降低多光子吸收的方法。
非线性光学 太赫兹 差频 双光子吸收 三光子吸收 激光与光电子学进展
2014, 51(3): 031901
山东科技大学理学院青岛市太赫兹技术重点实验室, 山东 青岛 266510
石墨烯特殊的零带隙能带结构和载流子弛豫特性,在研究太赫兹辐射源相干放大领域引起广泛关注。考虑带内和带间跃迁对电导率的贡献,研究了光抽运单层和多层石墨烯中非平衡二维电子空穴系统的动态电导率特性。结果表明,在足够强的光抽运下,石墨烯中的粒子数反转能够使得动态电导率的实部在太赫兹频段内出现负值,这使基于石墨烯的太赫兹放大或受激辐射源成为可能。同时,通过研究动量弛豫时间、温度、层数、光强对石墨烯的负动态电导率的影响表明,石墨烯多层结构的动态电导率最小值的绝对值更大,作为太赫兹激光器的激活介质更具优势。
激光技术 太赫兹 光抽运 石墨烯 负动态电导率
河南师范大学计算机与信息技术学院,河南新乡453007
鉴于邻域窗口影响二维阈值法的分割结果,提出了一种基于中值邻域二维最小交叉Tsallis熵的快速图像分割方法。首先利用中值滤波法构建中值邻域二维直方图;然后将最小交叉Tsallis熵运用在这种直方图上构建中值邻域二维最小交叉Tsallis熵分割法,由于中值滤波后的图像优于均值滤波后的图像,此法能获得更理想的阈值;最后将递推法与定义的数组运算相结合导出快速算法搜索最佳阈值向量,并用此阈值向量对原图像和中值邻域图像进行分割,得到更好的分割结果。实验结果表明:相对于当前均值邻域二维最小交叉Tsallis熵阈值法,该方法不仅分割效果更好,抗噪性更强,而且速度更快。
图像分割 二维最小交叉熵 Tsallis熵 中值邻域 递推算法 image segmentation 2-D minimum cross entropy Tsallis entropy median value neighborhood recursive algorithm





